RIPを使用したLinuxルータ構築方法
[概 要]
quaaga を使用することで、ルーティング経路を自動化したLinuxルータを構築することができます。
本ドキュメントでは、quaagaがサポートする複数のルーティングプロトコルの中で、RIP (Routing Information Protocol) を使用した、最も基本的なルーティングの設定方法について説明します。
・本ドキュメントではTCP/IP 、およびルーティングの基礎知識の説明は省略します。
・ルータにはNIC (Network Interface Card) が2枚以上付いているマシンが必要です。
Asianux Server 3 (x86版)
MIRACLE LINUX V4.0 (x86版)
本ドキュメントでは、以下の構成でclientA から clientB へ正しく通信が行われることを確認します。
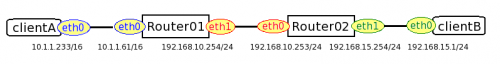
・クライアント(ClientA,B)、ルータ(Router01,02)とも、コマンド実行や設定は root 権限で実施します。
・IPv4 のルーティング設定を対象とします。
各ルーターにおいて、パケットフォワーディングの設定を有効にするために、/etc/sysctl.confファイルの、"net.ipv4.ip_forward” の値を1に設定します。
[変更前]
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 0
[変更後]
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
# sysctl -p
1.eth0/eth1 の NIC にIP アドレスとネットマスクを設定
IPアドレスとネットマスクの設定を行うには、CUIの場合はsystem-config-network-tui コマンド、X Window環境の場合はsystem-config-network-guiコマンドを実行します。
Name:eth0
Device:eth0
Use DHCP:無し
Static IP:10.1.1.61
Netmask:255.255.0.0
Default gateway IP:無し
Name:eth1
Device:eth1
Use DHCP:無し
Static IP:192.168.10.254
Netmask:255.255.255.0
Default gateway IP:無し
設定後OSを再起動してください。
詳細はAsianux Server 3 サーバー構築・運用ガイド を参照してください。
再起動後、設定が正しく行われているかifconfig等で確認します。
# ifconfig eth0
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:0C:29:5F:75:0F
inet addr:10.1.1.61 Bcast:10.1.255.255 Mask:255.255.0.0
inet6 addr: fe80::20c:29ff:fe5f:750f/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:908 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:252 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:90784 (88.6 KiB) TX bytes:31598 (30.8 KiB)
Interrupt:177 Base address:0x1400
# ifconfig eth1
eth1 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:0C:29:5F:75:19
inet addr:192.168.10.254 Bcast:192.168.10.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::20c:29ff:fe5f:7519/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:309 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:12 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:30176 (29.4 KiB) TX bytes:1432 (1.3 KiB)
Interrupt:185 Base address:0x1480
2.quaggaとripの設定ファイルを作成
/etc/quaggaディレクトリ以下にサンプルファイルが用意されていますので、ここではそれらをコピーして使用します。
# cd /etc/quagga/
# cp -p zebra.conf.sample zebra.conf
# cp -p ripd.conf.sample ripd.conf
3.quagga(zebra) サービスを起動
# service zebra start
zebra を起動中: Nothing to flush.
[ OK ]
※OS起動時にサービスを自動で起動するように設定するには下記を行います。
# chkconfig zebra on
4.ripd サービスを起動
# service ripd start
ripd を起動中: [ OK ]
※OS起動時にサービスを自動で起動するように設定するには下記を行います。
# chkconfig ripd start
5.quaggaの設定
対話的設定モードにログインし、設定を行います。
# vtysh
Hello, this is Quagga (version 0.98.6).
Copyright 1996-2005 Kunihiro Ishiguro, et al.
Router01.example.com#? ←"?” を入力すると、ヘルプが表示されます
clear Reset functions
configure Configuration from vty interface
copy Copy from one file to another
debug Debugging functions (see also 'undebug')
disable Turn off privileged mode command
end End current mode and change to enable mode
exit Exit current mode and down to previous mode
list Print command list
no Negate a command or set its defaults
ping Send echo messages
quit Exit current mode and down to previous mode
show Show running system information
ssh Open an ssh connection
start-shell Start UNIX shell
telnet Open a telnet connection
terminal Set terminal line parameters
traceroute Trace route to destination
undebug Disable debugging functions (see also 'debug')
write Write running configuration to memory, network, or terminal
設定モードに切り替えます。
Router01.example.com# configure terminal
RIP の経路情報を認証なしで受信するように eth1 に設定します
Router01.example.com(config)# interface eth1
Router01.example.com(config-if)# no ip rip authentication mode
Router01.example.com(config-if)# exit
RIP で提供する経路情報のネットワークを設定します
Router01.example.com(config)# router rip
Router01.example.com(config-router)# network 10.1.0.0/16
Router01.example.com(config-router)# network 192.168.10.0/24
Router01.example.com(config-router)# exit
設定した内容をファイルに書き込みます
Router01.example.com# write memory
Building Configuration...
Configuration saved to /etc/quagga/zebra.conf
Configuration saved to /etc/quagga/ripd.conf
[OK]
6.ルーティングテーブルの確認
この時点では、直接接続されているネットワーク情報しか表示されていません
Router01.example.com# show ip route
Codes: K - kernel route, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, O - OSPF,
I - ISIS, B - BGP, > - selected route, * - FIB route
C>* 10.1.0.0/16 is directly connected, eth0
C>* 127.0.0.0/8 is directly connected, lo
C>* 192.168.10.0/24 is directly connected, eth1
1.eth0/eth1 の NIC にIP アドレスとネットマスクを設定
Router01と同様にeth0/eth1 の NIC に対して IP アドレスとネットマスクを設定します。
system-config-network-tui コマンドまたは、system-config-network-guiコマンドを使用して、eth0/eth1 の NIC に対して IP アドレスとネットマスクを設定します。
Name:eth0
Device:eth0
Use DHCP:無し
Static IP:192.168.10.253
Netmask:255.255.255.0
Default gateway IP:無し
Name:eth1
Device:eth1
Use DHCP:無し
Static IP:192.168.15.254
Netmask:255.255.255.0
Default gateway IP:無し
設定後OSを再起動してください。
2.ルーティング設定
同様にルーティング設定を行います。
quagga(zebra) と rip の設定ファイルをサンプルからコピーします
# cd /etc/quagga/
# cp -p zebra.conf.sample zebra.conf
# cp -p ripd.conf.sample ripd.conf
quagga(zebra) と ripd サービスを起動させます
# service zebra start
# service ripd start
quagga(zebra) と ripd サービスを自動起動させます
# chkconfig zebra on
# chkconfig ripd on
設定モードに切り替えて、RIP の経路情報を設定します
# vtysh
Router02.example.com# configure terminal
Router02.example.com(config)# interface eth0
Router02.example.com(config-if)# no ip rip authentication mode
Router02.example.com(config-if)# exit
Router02.example.com(config)# router rip
Router02.example.com(config-router)# network 192.168.10.0/24
Router02.example.com(config-router)# network 192.168.15.0/24
Router02.example.com(config-router)# exit
Router02.example.com(config)# exit
Router02.example.com# write memory
Building Configuration...
Configuration saved to /etc/quagga/zebra.conf
Configuration saved to /etc/quagga/ripd.conf
[OK]
3.経路情報受信の確認(Router02)
Router01 から受信した 10.1.0.0/16 の経路情報が、ルーティングテーブルに追加されていることを確認します。
Router02.example.com# show ip route
Codes: K - kernel route, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, O - OSPF,
I - ISIS, B - BGP, > - selected route, * - FIB route
R>* 10.1.0.0/16 [120/2] via 192.168.10.254, eth0, 00:00:12
C>* 127.0.0.0/8 is directly connected, lo
C>* 192.168.10.0/24 is directly connected, eth0
C>* 192.168.15.0/24 is directly connected, eth1
4.経路情報受信の確認(Router01)
同様に Router01 において、再度ルーティングテーブルを確認すると、 Router02 から受信した 192.168.15.0/24 の経路情報が追加されています。
Router01.example.com# show ip route
Codes: K - kernel route, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, O - OSPF,
I - ISIS, B - BGP, > - selected route, * - FIB route
C>* 10.1.0.0/16 is directly connected, eth0
C>* 127.0.0.0/8 is directly connected, lo
C>* 192.168.10.0/24 is directly connected, eth1
R>* 192.168.15.0/24 [120/2] via 192.168.10.253, eth1, 00:02:15
1.クライアントAのIPアドレス、ネットマスク、デフォルトゲートウェイの設定を行います。
system-config-network-tui コマンドまたは、system-config-network-guiコマンドを使用して、eth0の NIC に対して IP アドレスとネットマスクを設定します。
Name:eth0
Device:eth0
Use DHCP:無し
Static IP:10.1.1.233
Netmask:255.255.0.0
Default gateway IP:10.1.1.61
設定後OSを再起動してください。
2.クライアントBのIPアドレス、ネットマスク、デフォルトゲートウェイの設定を行います。
system-config-network-tui コマンドまたは、system-config-network-guiコマンドを使用して、eth0の NIC に対して IP アドレスとネットマスクを設定します。
Name:eth0
Device:eth0
Use DHCP:無し
Static IP:192.168.15.1
Netmask:255.255.255.0
Default gateway IP:192.168.15.254
設定後OSを再起動してください。
clientA から clientB へ ping 応答を確認します。
# ping 192.168.15.1
PING 192.168.15.1 (192.168.15.1) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 192.168.15.1: icmp_seq=0 ttl=62 time=2.62 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.15.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=62 time=0.822 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.15.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=62 time=2.12 ms
(Ctrl + C)
--- 192.168.15.1 ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2001ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.822/1.857/2.628/0.761 ms, pipe 2
clientA から clientB への経路情報を確認します。
# traceroute -n 192.168.15.1
traceroute to 192.168.15.1 (192.168.15.1), 30 hops max, 38 byte packets
1 10.1.1.61 0.354 ms 0.516 ms 0.220 ms
2 192.168.10.253 0.460 ms 0.402 ms 0.743 ms
3 192.168.15.1 3.903 ms 0.870 ms 0.641 m
ルーティング設定で重要な事は、往復の経路情報を必ず設定することです。
本ドキュメントの例では、Router01,Router02がお互い、自分が接続している全てのネットワークの経路情報を RIP で提供しているという点が重要です。
複雑なネットワークになると、復路の経路情報を見落とすことがあるため、「ルーターが直接接続しているネットワークの経路情報を発信しない限り、ルーティングは行われない」ということを注意する必要があります。
2007年 3月27日 新規作成